Introduction to Database file writing
You can update the project database file with every respondent entry. Every respondent should have a separate row in the file, the new data can be access with online db_read.
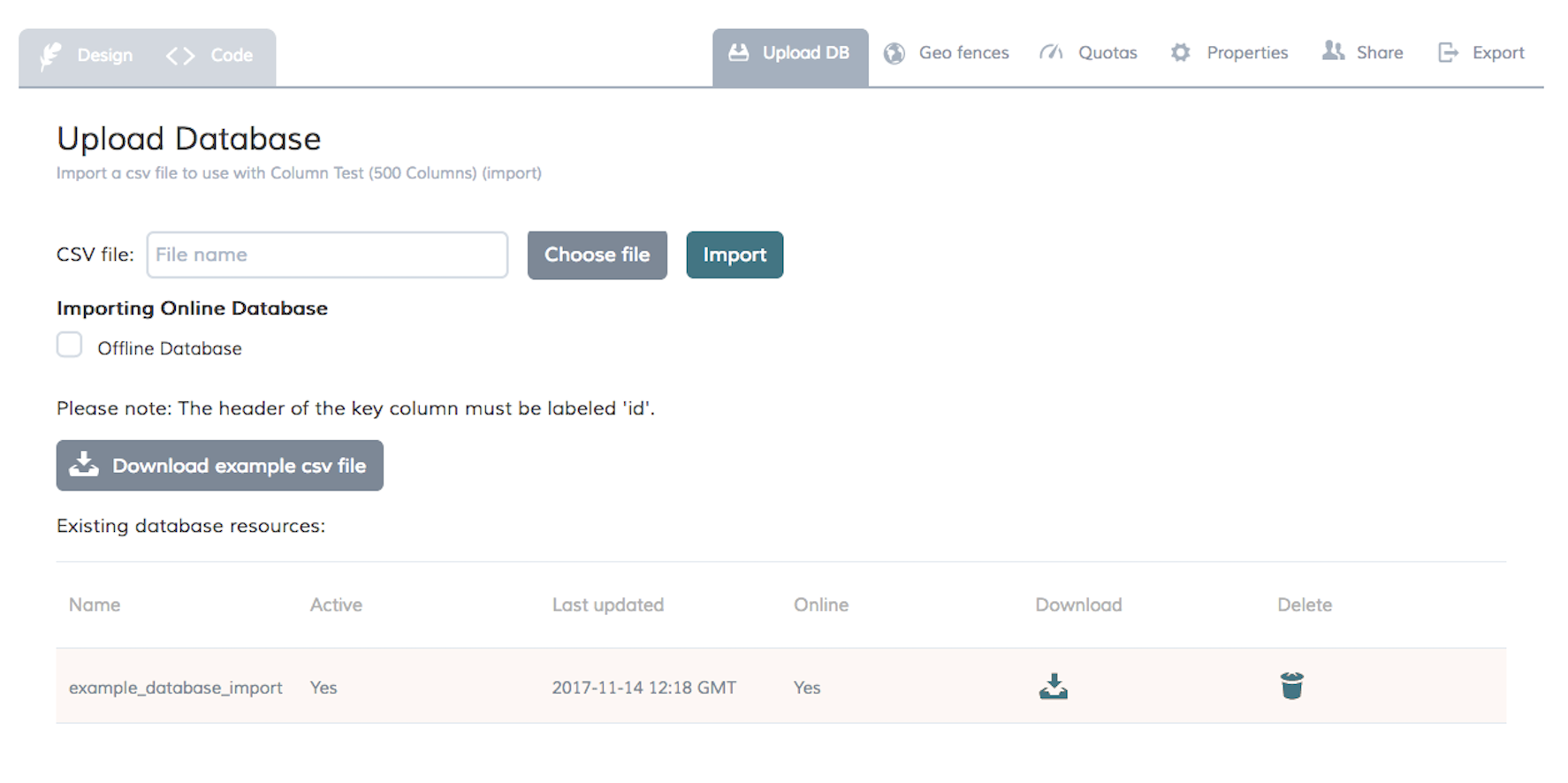
The database files can be downloaded using the corresponding button to the right.
Function Syntax
db_write(db_name,key,'value1','value2','value3',...)
Use when all column values are being updated.
| Name | Description |
| db_name | The file name of the uploaded database. Do not include the .csv extension in this parameter. |
| key | This is the field to be searched in the database. This can be a question answer, survey variable, sample field, etc... |
| 'value1','value2',... | Value to be written. Values should be put in the same order of the columns. All columns must have a value in this function. This could be answer(), local or global variable, date and time functions. |
db_write(db_name,key,dbcol(col1,'value1'),dbcol(col2,'value2),...)
Use when specific columns needs to be updated. could handle up to 500 columns
| Name | Description |
| db_name | The file name of the uploaded database. Do not include the .csv extension in this parameter. |
| key | This is the field to be searched in the database. This can be a question answer, survey variable, sample field, etc... |
| dbcol(col1,'value1') | This function write a value into the specified column. Replace col1 with the column header. 'value1' could be answer(), local or global variable, date and time functions. |
General rules
- Always use the db-functions in a postcondition.
- Database names are case sensitive when used in a condition.
- The values could include any special character except the following:
{ {
} }
( (
) )
[ [
] ]
< <
> >
\ \
' ''
- Do not allow multiple respondents to write data into the same field! We recommend that data for each respondent is written to its own row, this is done with db_write() and getrespdata()
then="db_write(example_database_import,getrespdata(username),'Donald','Duck','1313 Webfoot Walk','Duckburg','Calisota')"/>
- Do not use barcode_lookup() and db_read() in the same survey, this causes db_read to read cached data.
- Empty space, e.g. an empty open text question written to the database results in a single quotation mark if you pipe it and in the 'upload db report'. It is best if you check that an answer is given before you write it into the database file.
- The column limit in sqlite is one thousand characters (but there might be limitations on the end user's device memory and on the data transfer capabilities).
Example use case
- On Shopping Diaries, update products’ list.
When the lookup returns ‘0’ to indicate the barcode was not found, add the new product barcode and then fill in the rest of the columns with the following answers.
- Fill in attendance list
When a respondent join, add their name and information into a new row. You’ll end up with attendance list.
- Summary across respondents
Add every respondent input into a row and read all rows at once in one screen that is displayed to all respondents. Use independent id for these rows from the username.
